If you’ve ever heard that eyes are windows to the soul, modern AI shows they’re also windows to your health. In this guide, I’ll break down what ai tools analyze ocular biomarkers for health screening, why they matter, and how they’re used in clinics today. I’ve helped deploy retina AI in telemedicine pilots, and I’ll share lessons from the field so you can make informed decisions with confidence. Expect clear examples, up-to-date insights, and a human take on a complex topic.
Source: www.poudrevalleyeyecare.com
What Are Ocular Biomarkers And Why They Matter
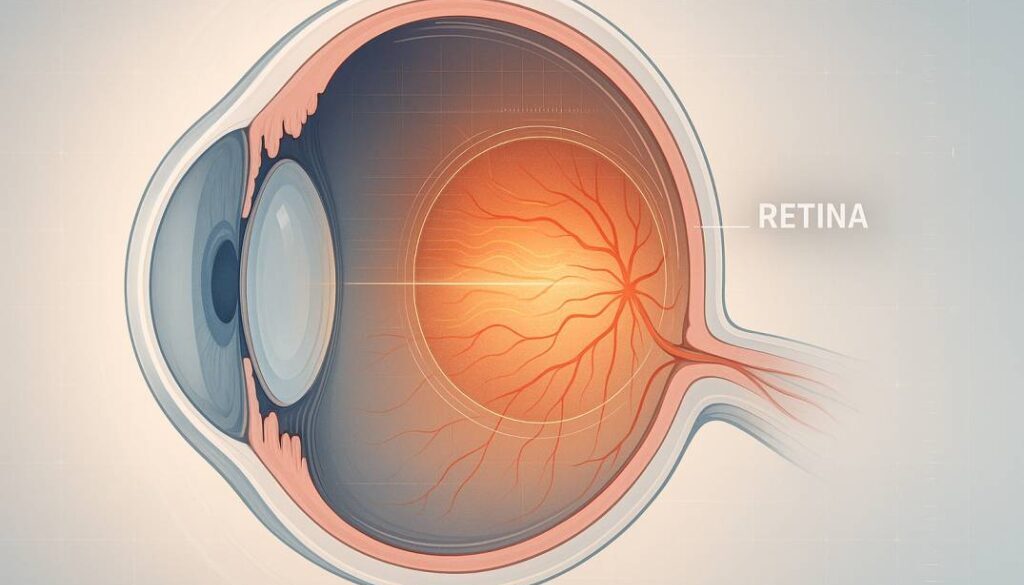
Ocular biomarkers are measurable features in or around the eye that signal health status. AI turns these subtle patterns into useful insights.
Common ocular biomarkers AI can analyze:
- Retina and vessels Signs of diabetic retinopathy, hypertension, and cardiovascular risk from microaneurysms, hemorrhages, vessel caliber, tortuosity, and arteriovenous nicking.
- Optic nerve head Indicators of glaucoma from cup-to-disc ratio, rim thinning, and nerve fiber layer defects.
- Macula Fluid, drusen, and pigment changes tied to diabetic macular edema and age-related macular degeneration.
- Cornea and nerves Changes linked to neuropathy and diabetes severity from corneal confocal microscopy.
- Tear film and meibomian glands Dry eye disease patterns from meibography and tear stability.
- Pupillary response Neurologic and autonomic insights from light reflex dynamics.
- Hyperspectral/retinal signatures Emerging signals for neurodegeneration risk in research settings.
AI helps because many of these features are too subtle for quick human review at scale. With the right images, algorithms spot early disease and risk long before symptoms show.
Source: www.mdpi.com
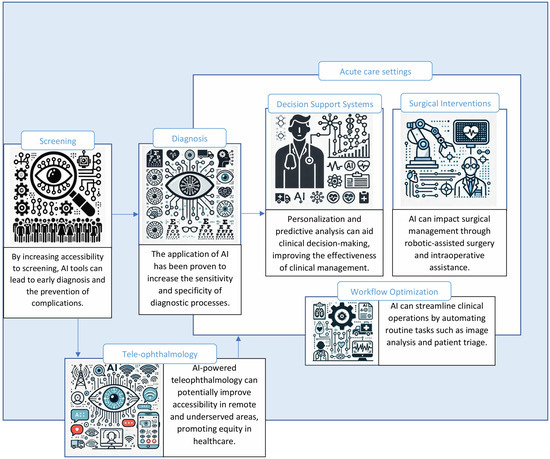
How AI Sees The Eye: Modalities And Methods
Modern ocular AI draws on a mix of image types and models.
Main imaging modalities:
- Color fundus photographs Fast, wide use in primary care and tele-ophthalmology for diabetic eye disease and vascular risk.
- Optical coherence tomography OCT cross-sections of the retina and optic nerve for macular disease and glaucoma.
- Ultra-widefield imaging Peripheral retina screening for lesions missed in standard fields.
- Corneal confocal microscopy High-resolution corneal nerve images for neuropathy assessment.
- Meibography and tear film imaging Structure and stability for dry eye.
- Hyperspectral imaging Research-only for Alzheimer’s and amyloid markers.
Typical AI methods:
- Convolutional neural networks Detect lesions and classify disease stages.
- Transformer and foundation models Pretrained on large eye datasets to generalize across devices.
- Multimodal fusion Combine images with basic clinical data for stronger predictions.
- Explainability tools Heatmaps and lesion overlays to build trust and support clinical review.
In practice, the best systems balance accuracy with workflow fit: fast capture, simple outputs, and actionable referrals.
Source: www.thno.org
Top AI Tools And Platforms You Should Know
Below are representative tools used or studied for ocular biomarker screening. Always verify local approvals and indications.
Autonomous Diabetic Retinopathy Screening: IDx-DR (Digital Diagnostics)
– What it does Autonomous detection of more-than-mild diabetic retinopathy from fundus photos. FDA-cleared for use without an eye specialist on-site.
– Why it matters Enables primary care screening, closing care gaps and boosting early referrals.
– Tip from experience Ensure good image quality with two fields per eye. Train staff on capture and retry logic.
Autonomous DR Screening: EyeArt (Eyenuk)
– What it does Detects diabetic retinopathy and macular edema risk from fundus images. FDA-cleared with broad global use.
– Why it matters High sensitivity supports safe triage, even in busy clinics.
– Tip Watch for mydriasis protocols in darker irides or small pupils to reduce ungradable rates.
OCT-Based Triage: Moorfields/DeepMind-Style Models
– What it does AI triage of OCT scans across many retinal conditions with referral recommendations. Widely validated in peer-reviewed research and integrated into vendor workflows.
– Why it matters Fast prioritization helps manage backlogs and improves time to treatment.
Glaucoma And Nerve Fiber Layer AI
– What it does AI estimates cup-to-disc ratio and nerve fiber thinning from fundus and OCT, assisting glaucoma risk assessment.
– Where you’ll see it Built into device ecosystems and practice software to flag suspects for full workup.
Cardiovascular Risk From the Retina
– What it does AI estimates heart risk factors like age, blood pressure class, and risk of events from fundus images using vessel features. Large biobank studies show strong signal.
– Use case Opportunistic risk screening during eye exams or primary care imaging.
Corneal Nerve AI For Peripheral Neuropathy
– What it does Automated corneal nerve metrics from confocal microscopy correlate with diabetic neuropathy severity.
– Why it matters Offers noninvasive tracking of small fiber neuropathy.
Dry Eye And Meibography AI
– What it does Classifies meibomian gland dropout and tear film stability to guide dry eye therapy plans.
– Tip Pair with symptom surveys to personalize treatment.
Alzheimer’s And Neurodegeneration: Research-Stage Tools
– What it does Hyperspectral and retinal texture analysis for amyloid signatures and cognitive risk. Promising, but not yet for routine clinical decisions.
– Caveat Use within research protocols and avoid overinterpreting single scans.
Smartphone And Portable Fundus + AI
– What it does Phone-based or portable cameras with embedded AI for field screening in community settings.
– Why it matters Extends reach to workplaces, pharmacies, and rural clinics.
From my tele-ophthalmology rollout, the biggest wins came from pairing autonomous DR AI with a simple two-camera workflow and clear referral rules. The unglamorous parts staff training, lighting, and patient flow drove more value than tiny accuracy gains.
Source: www.philips.com
Real-World Workflows: From Capture To Care
Here’s a simple playbook you can adapt.
- Set the scope Start with one use case, like DR screening for all adults with diabetes in primary care.
- Choose the hardware Go with a nonmydriatic fundus camera with beginner-friendly autofocus and alignment aids.
- Validate image quality Use built-in quality checks and a protocol for retakes and pharmacologic dilation if needed.
- Integrate results Send structured results into the EHR with clear categories no disease, refer soon, urgent refer.
- Close the loop Track referrals, schedule follow-ups, and give patients a one-page summary with next steps.
- Monitor performance Review ungradable rates, sensitivity/specificity vs. adjudication samples, and demographic fairness.
- Educate the team Create quick guides for image capture and a script for sharing results with patients.
A quick example In a community clinic, we screened 75% of eligible patients during routine visits. Ungradable rates fell from 18% to 6% after hands-on coaching and better lighting. The biggest surprise Patients were more likely to attend referrals when given printed AI overlays that “showed the spots.”
Data Quality, Bias, Privacy, And Regulation
To keep trust high, plan for the non-technical details.
- Bias and fairness Validate on your local population. Check performance by age, sex, skin tone, and media opacity. Tune workflows to reduce bias in image quality.
- Privacy and security Confirm HIPAA compliance, encryption, and data minimization. Prefer on-device processing when bandwidth is limited.
- Regulatory status Confirm FDA clearance or CE mark for your indication. Use research-only tools within IRB-approved protocols.
- Explainability Provide clinicians with heatmaps and textual reasons for decisions where available, and set escalation rules.
- Maintenance Monitor drift. Update software on a controlled cadence and retrain if device mix or patient profile changes.
Transparent communication matters. Tell patients what the AI does, what it doesn’t, and how a human clinician remains in the loop.
Buying And Implementation Checklist
Use this short checklist to compare vendors.
- Clinical fit Indication, performance metrics, ungradable handling, referral thresholds.
- Workflow fit Capture time, staff training hours, EHR integration, report formats.
- Technical fit Camera compatibility, on-prem vs. cloud, API options, uptime SLAs.
- Safety and quality Regulatory status, post-market surveillance, audit logs.
- Cost and ROI Subscription vs. per-scan pricing, hardware costs, reimbursement pathways, expected savings and prevented vision loss.
- Support Onboarding, remote monitoring, and response times.
Pro tip Pilot with 50 to 100 patients before scaling. Measure image quality, throughput, and referral accuracy. In my experience, a small pilot answers 80% of questions you won’t find in brochures.
What’s Next: Trends To Watch
The field is moving fast. Keep an eye on these shifts.
- Foundation models Large retinal models pre-trained on millions of images will improve generalization across devices and clinics.
- Multidisease panels One image, many outputs DR, glaucoma risk, AMD, and cardiovascular signals on a single report.
- Home and retail capture Patient-operated devices in pharmacies and at home will expand access.
- Neuro-ophthalmic signals Better pupillometry and eye-movement AI for concussion, autonomic issues, and early cognitive change.
- Payment innovation More clear reimbursement pathways will drive adoption beyond pilots.
The north star remains the same earlier detection, simpler workflows, and fewer patients lost to follow-up.
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Ai Tools Analyze Ocular Biomarkers For Health Screening
Q. Which AI tools are FDA-cleared for eye disease screening?
IDx-DR and EyeArt are FDA-cleared for autonomous diabetic retinopathy screening. Several OCT triage tools and embedded device algorithms assist clinicians but may not be autonomous or approved for all indications.
Q. Can AI find heart risk from my eye photos?
Yes, research shows retinal images carry signals for cardiovascular risk. Some systems estimate risk factors from vessel features. These tools are emerging; confirm clinical approvals and use them to support, not replace, standard risk scoring.
Q. Does AI replace an eye doctor?
No. Even autonomous systems work within defined tasks and referral thresholds. Clinicians interpret results, confirm diagnoses, and manage treatment. AI is a force multiplier, not a substitute.
Q. What images do I need for AI eye screening?
Most DR tools use two 45-degree fundus photos per eye. Glaucoma and macular disease tools often need OCT. Dry eye uses meibography and tear film videos. Follow the vendor’s capture protocol for best results.
Q. How accurate are these tools?
Top systems report high sensitivity and strong specificity for their indicated use. Real-world performance depends on image quality, device type, and population. Validate locally and track outcomes.
Q. Is my data safe?
Choose vendors with HIPAA-compliant workflows, encryption, and clear data retention policies. Ask for a security overview and audit logs before deployment.
Q. Can I use a smartphone camera?
Yes, with smartphone fundus adapters and compatible AI. Image quality varies by device and user skill. Pilot first to ensure reliable gradable rates.
Conclusion
AI is turning the eye into a fast, noninvasive health screen that reaches more people where they already get care. Start with a focused use case like diabetic retinopathy, pick a camera your staff can master in a day, validate results on your population, and keep a clear referral loop. The payoff is real fewer missed cases, quicker care, and patients who finally see what’s at stake.
Ready to explore more? Subscribe for updates, share your experience in the comments, or reach out if you want a practical checklist to kick off your pilot.
Watch This Video on what ai tools analyze ocular biomarkers for health screening
>>> Get More Review Here: What is The Best Answer Engine Optimization Tool For AI Products <<<
